
Confused about fire blanket standards? Our detailed comparison breaks down EN 1869:2019, GA 1205-2014, and ASTM F1989. Discover why the European EN 1869 standard is the most rigorous for suppressing cooking oil fires, how the Chinese GA 1205 compares, and why the US ASTM standard may be less effective. Learn which certification to look for to ensure maximum safety.
Keywords:
Fire blanket standards, EN 1869, GA 1205, ASTM F1989, fire blanket test, cooking oil fire, fire blanket certification, which fire blanket is best, fire safety, fire blanket performance, Class F fire, fire blanket comparison
| Test Parameter |
Chinese Standard GB 8624 / GA(XF) 1205-2014 |
US Standard ASTM F1989-05 (2013) |
European Standard EN 1869:2019 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fire Type | Cooking Oil Fire (Class F) | Cooking Oil Fire (Class F) | Cooking Oil Fire (Class F) |
| Pan Material | Steel | Steel | Steel |
| Pan Dimensions | Bottom Ø 57 cm, H 10 cm | Ø 51 cm (20 in), D 7.6 cm (3 in) | Ø 57 cm, H 10 cm |
| Fuel Type | Edible Vegetable Oil (e.g., Soybean) | Edible Vegetable Oil (e.g., Corn) | Edible Vegetable Oil (e.g., Sunflower) |
| Fuel Depth | 4 cm | 1.27 cm (0.5 in) | 4 cm |
| Fuel Volume | ~10 Liters | ~2.5 Liters | ~10 Liters |
| Pre-heat Temperature | (330 ± 5) °C | 288 °C (550 °F) | (330 ± 5) °C |
| Pre-burn Time | 60 seconds | 30 seconds | 60 seconds |
| Post-application Observation Time | 1 minute | Immediate Inspection | 5 minutes |
| Pass/Fail Criteria | No re-ignition. Blanket must not burn through or melt. Charring without flame is acceptable. | Fire is extinguished. | No re-ignition. Blanket must not burn through or melt. Charring without flame is acceptable. |
| Other Tests | Includes flammability, mechanical strength, corrosion resistance. | Primarily focused on fire extinction performance. | Includes thermal stability, flexibility, mechanical strength (more comprehensive). |
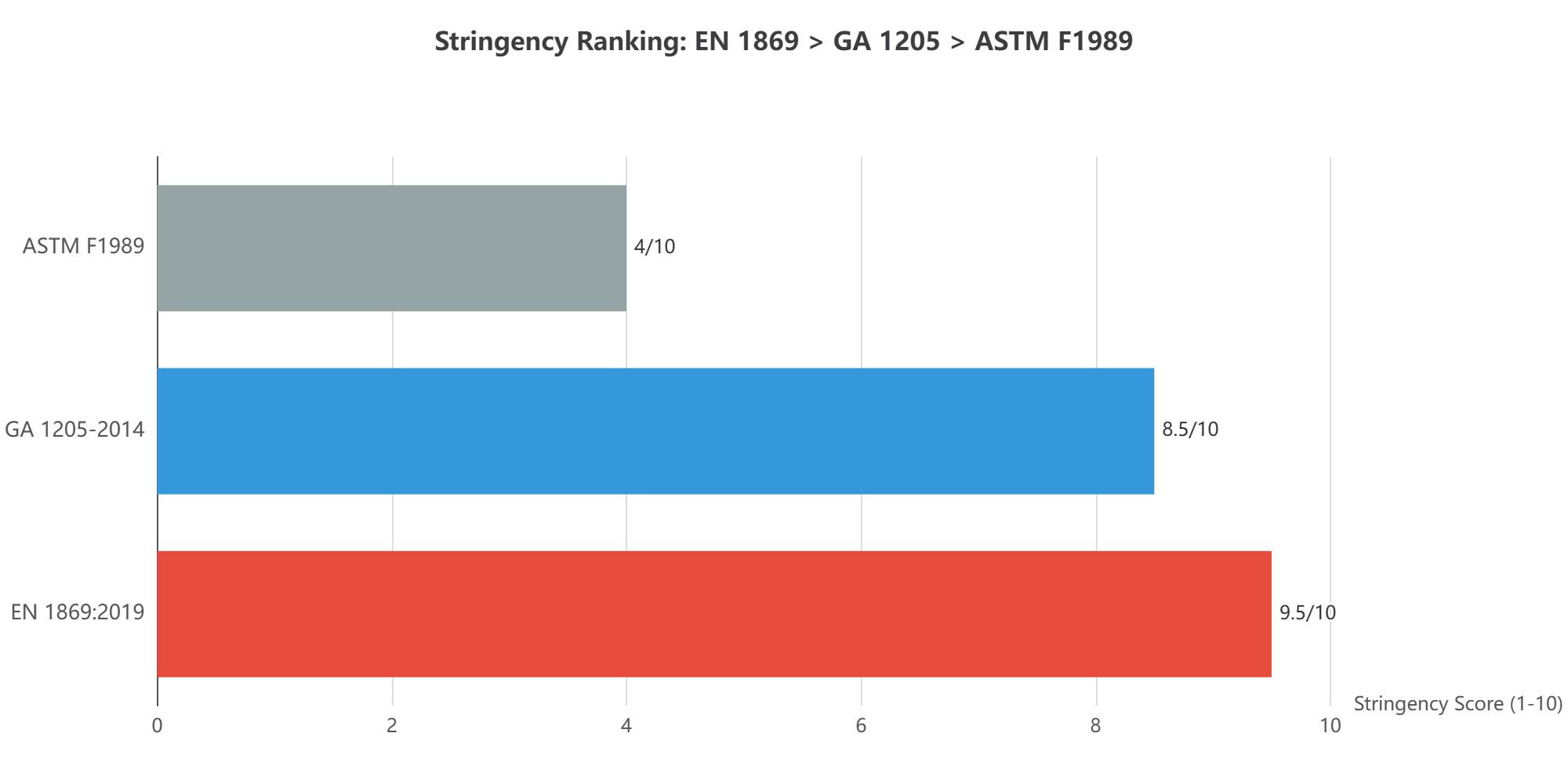
1. Ranking of Stringency: EN 1869:2019 > GA 1205-2014 > ASTM F1989
EN 1869:2019 is the most stringent. Its high oil temperature (330°C), deep oil layer (4cm), long pre-burn time (60s), and crucially, the 5-minute observation period place extreme demands on the blanket's smothering effectiveness and anti-reflash capability. Any minor flame recovery or blanket failure will cause test failure.
GA 1205-2014 aligns closely with the EN standard in initial fire suppression conditions (same oil temp, depth, pre-burn time). The key difference is the shorter 1-minute observation time. This means the Chinese standard is equally tough on "instantly suppressing a large fire" but slightly less demanding than EN 1869 on long-term "preventing re-ignition" reliability.
ASTM F1989 has the most lenient requirements. Its lower oil temperature (288°C), very shallow fuel depth (1.27cm), shorter pre-burn time (30s), and lack of a defined reflash observation period mean the fire itself is smaller and contains less energy, making it easier to suppress, thus presenting a less challenging test for the blanket.
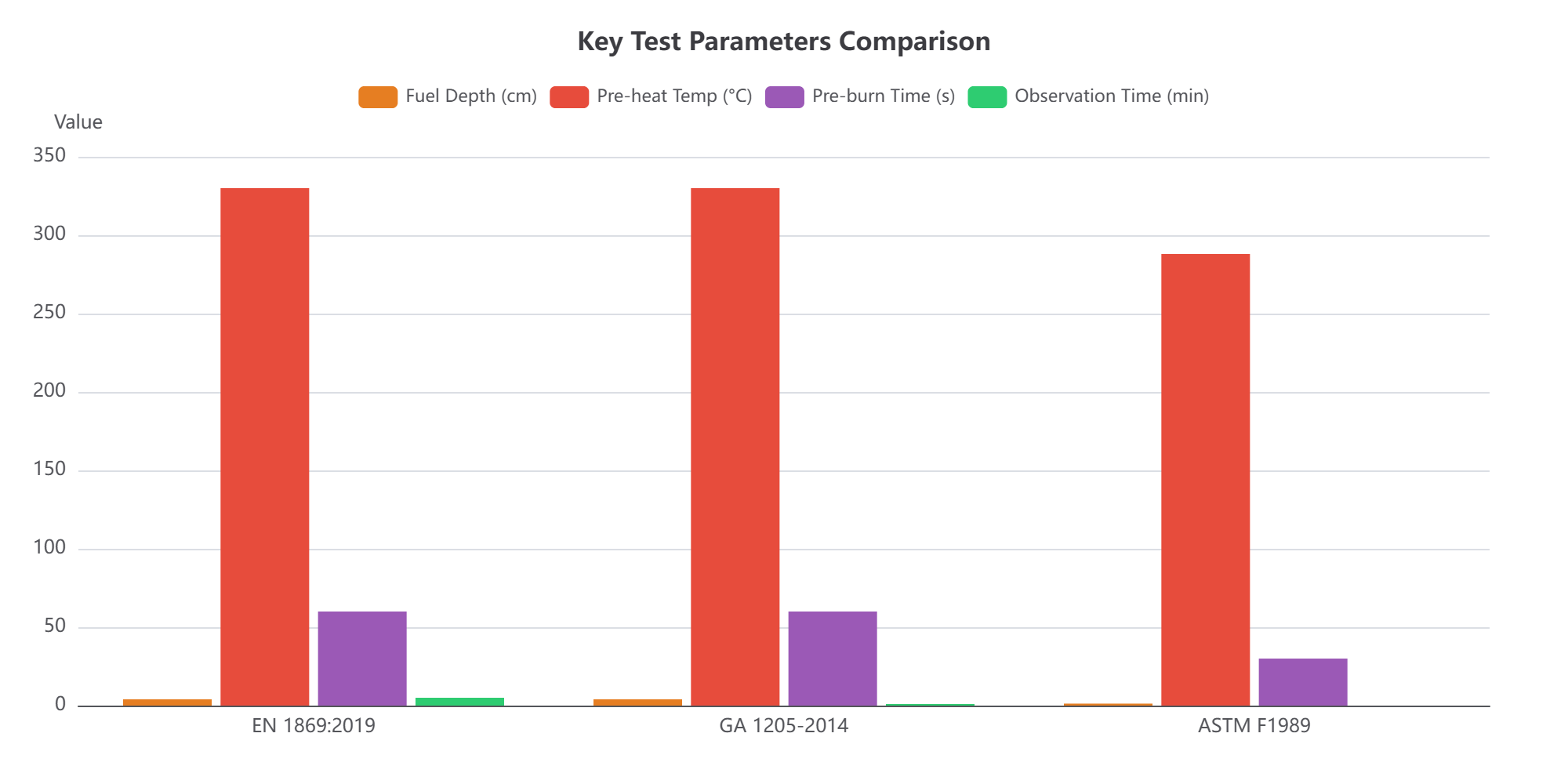
2. Key Differences Analysis:
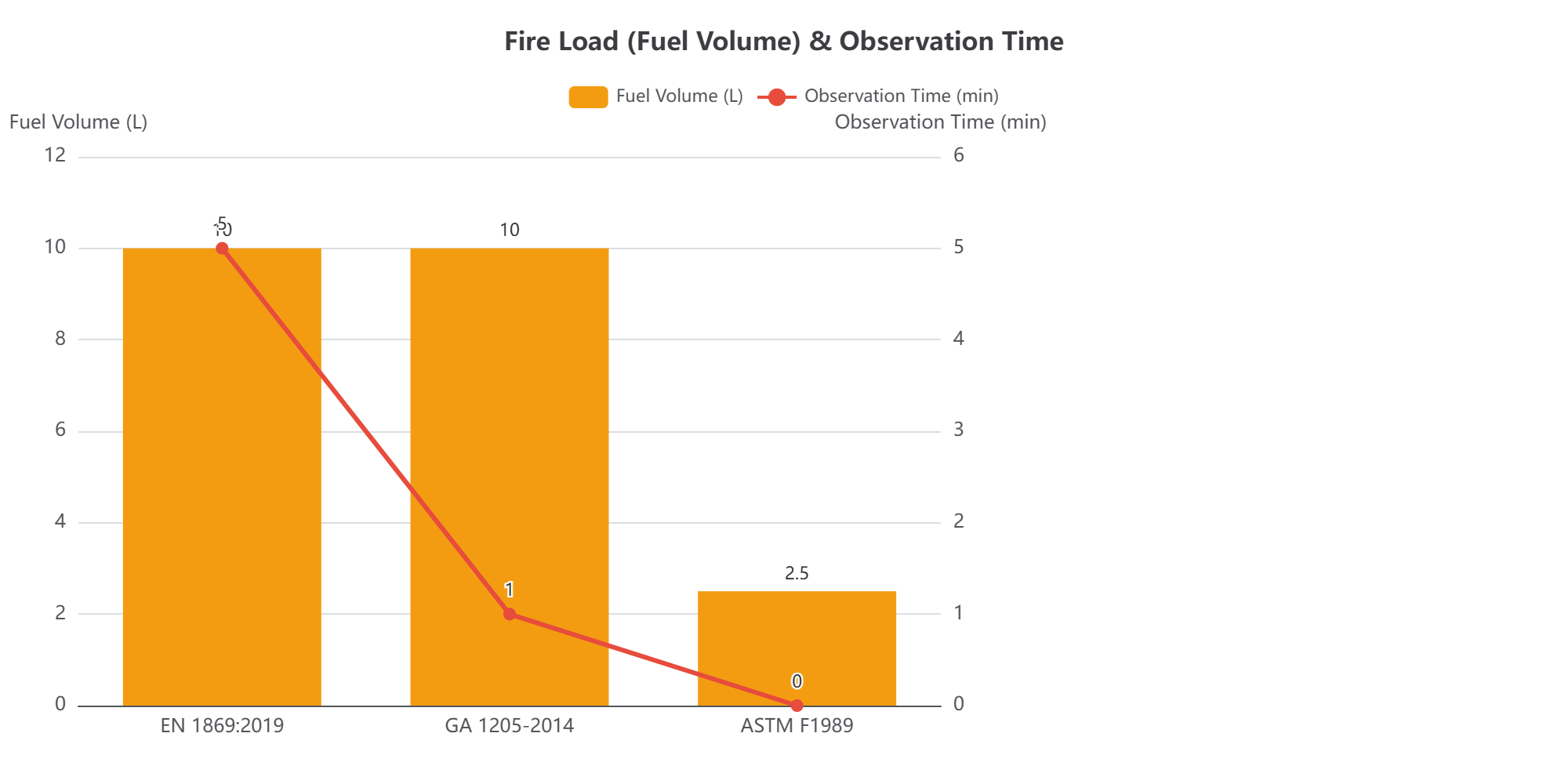
Fuel Depth & Volume: This is the most significant difference. A 4cm deep fire (~10L oil) has a much higher fire load and thermal energy than a 1.27cm deep fire (~2.5L oil). It burns more vigorously and retains significantly more heat after suppression, drastically increasing the risk of re-ignition.
Observation Time: A 5-minute observation period (EN) is far more rigorous than 1 minute (CN) or none (US). It better simulates the real-world scenario where a blanket is left in place while waiting for the fire department or for the heat source to cool down, thoroughly testing the product's sustained effectiveness.
Testing Philosophy: The European and Chinese standards aim to simulate more realistic and extreme fire conditions, whereas the US standard functions more as a basic "pass/fail" test.
A fire blanket certified to both EN 1869:2019 and GA 1205-2014 typically indicates superior and more reliable performance, especially in the critical area of preventing cooking oil re-ignition. If a product only complies with the ASTM standard, its effectiveness in a severe fire scenario may be questionable. Consumers should prioritize products that certify compliance with the European (EN) or Chinese (GA) standards.
2nd Floor, No. 2 Standard Workshop, Hengke Industrial Park Phase I,Ganzhou Economy and Technology Development Zone, Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province, P.R. China
 赣公网安备36072402000211号
赣公网安备36072402000211号