
Abstract
Fire safety is a critical concern in both residential and commercial settings, with the choice of suppression tool significantly impacting emergency outcomes. This paper provides a comparative analysis of fiberglass fire blankets against conventional dry powder and liquid fire extinguishers, evaluating key parameters including operation mechanism, usability, maintenance, and compliance with safety standards.
1. Operation Mechanism and Effectiveness
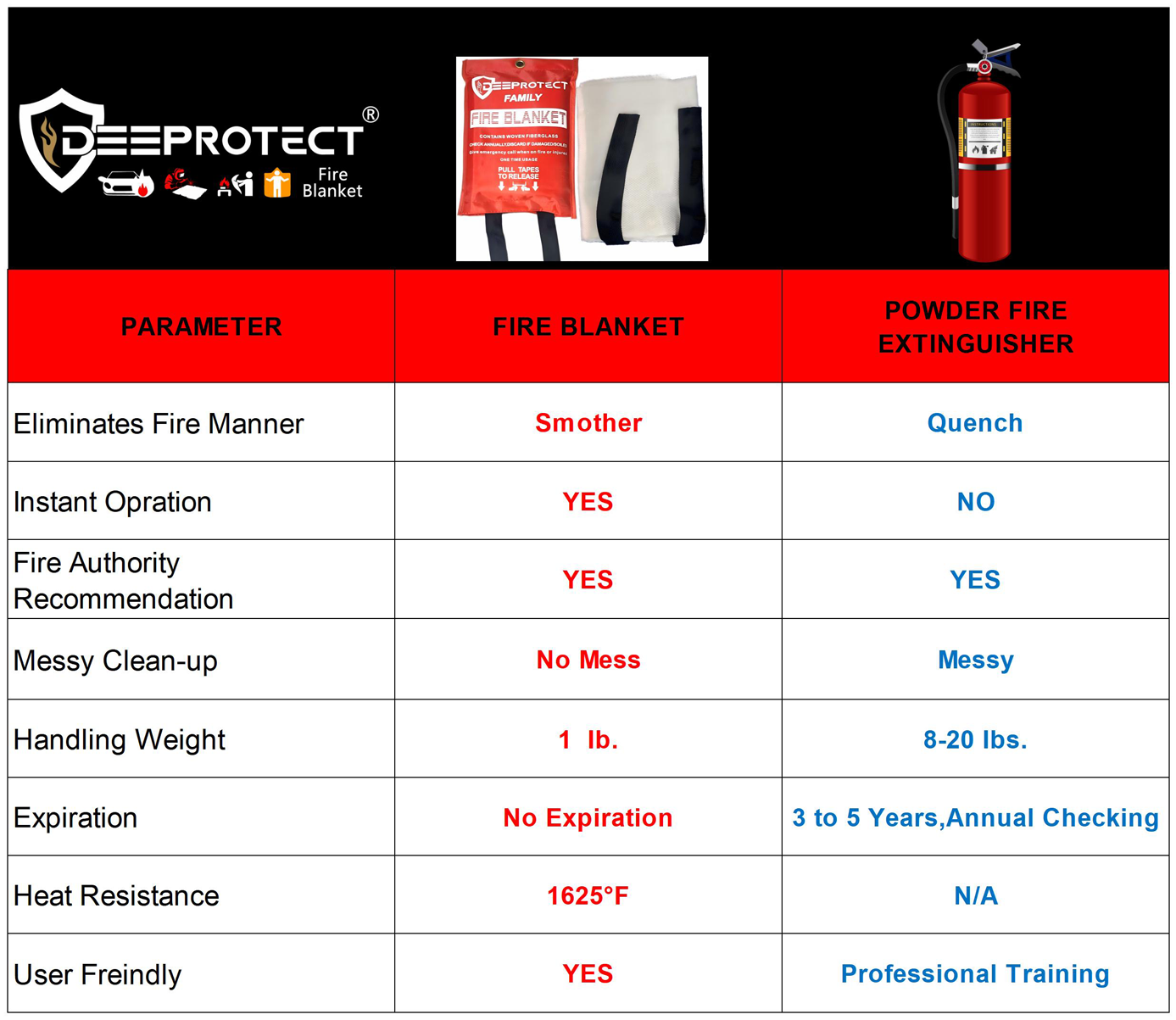
Fire blankets, typically constructed from fiberglass coated with a fire-retardant film, function primarily by smothering the fire, cutting off the oxygen supply. This method is exceptionally effective on Class F (cooking oils and fats) and small Class A (solid combustibles) fires. Standards such as EN 1869:2019 and GA 1205-2014 govern their performance, requiring them to withstand extreme heat—often up to 1625°F (885°C)—and effectively extinguish standardized oil fire tests without re-ignition.
In contrast, dry powder extinguishers (e.g., ABC type) operate by quenching the fire. They release a fine powder that interrupts the chemical chain reaction of the fire. While versatile against Class A, B, C, and electrical fires, they create a significant mess, and the powder can be corrosive and hazardous if inhaled. Liquid extinguishers, often water-based with additives, work by cooling the burning material but are ineffective and dangerous for grease, electrical, or liquid fuel fires.
2. Usability and User-Friendliness
The fire blanket's superiority in usability is evident across several parameters, as illustrated in the provided comparison.
Instant Operation & Training: Fire blankets offer "instant operation." Their use is intuitive—simply pull from the pouch and place over the flames—requiring minimal prior training. This makes them highly accessible to untrained individuals in a panic situation. Dry powder extinguishers, while also recommended by fire authorities, often require the user to remember the P.A.S.S. (Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep) technique, which can be forgotten under stress. Professional training is strongly advised for effective and safe use.
Weight and Handling: A typical fire blanket weighs around 1 lb. (0.45 kg), making it easy for almost anyone to handle and deploy swiftly. Dry powder extinguishers are significantly heavier, ranging from 8 to 20 lbs. (3.6 to 9 kg), which can hinder operation for children, the elderly, or those with limited strength.
Post-Fire Clean-up: The clean-up process starkly differentiates these tools. Fire blankets result in no mess, leaving only the burnt residue of the fire itself. Dry powder extinguishers, however, are notoriously messy. The fine powder infiltrates every crevice, is difficult to clean, and can cause damage to electronics and soft furnishings. Liquid extinguishers, if used inappropriately, can also cause water damage.
3. Maintenance and Long-Term Cost
Maintenance requirements are a crucial factor for long-term preparedness.
Expiration and Inspection: Fire blankets have a significant advantage as they typically have no expiration date if stored properly in their protective pouch and remain undamaged. They require only periodic visual checks for integrity. Conversely, dry powder extinguishers have a service life of 3 to 5 years and often require annual professional checking and recharging, incurring ongoing costs. The powder can also compact over time, rendering it ineffective.
4. Applicability and Limitations
Each tool has its ideal application scenario.
Fire Blankets are the unequivocal best choice for:
Kitchen fires (grease, pan fires).
Small contained fires (waste bin fires).
Wrapping around a person whose clothing is on fire.
Their limitations include ineffectiveness on large, spreading fires or deep-seated Class A fires.
Dry Powder Extinguishers offer broad-spectrum capability, making them suitable for:
Garage, workshop, or vehicle fires.
Electrical fires.
Fires involving flammable liquids.
Their limitations include the risk of inhalation hazards, reduced visibility during discharge, and the extensive clean-up required.
5. Conclusion
While both fire blankets and dry powder/liquid extinguishers are recommended by fire authorities, they serve complementary roles. The fiberglass fire blanket stands out for its simplicity, zero maintenance, clean operation, and exceptional effectiveness on common kitchen fires, as validated by stringent standards like EN 1869. It is the most user-friendly primary defense tool for households and food service establishments.
Dry powder extinguishers remain an essential, versatile tool for tackling a wider variety of fire types but come with the trade-offs of required training, heavy weight, mandatory maintenance, and messy residue. An optimal fire safety plan should include both: a fire blanket for immediate, simple response to cooking fires, and a appropriately rated extinguisher for broader, more complex fire risks.
---
References:
1. European Committee for Standardization. (2019). EN 1869:2019 - Fire blankets.
2. Ministry of Public Security of China. (2014). GA 1205-2014 - Fire blankets.
3. National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). Standard for Portable Fire Extinguishers (NFPA 10).
2nd Floor, No. 2 Standard Workshop, Hengke Industrial Park Phase I,Ganzhou Economy and Technology Development Zone, Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province, P.R. China
 赣公网安备36072402000211号
赣公网安备36072402000211号